Application scenarios
Chemical Dissolution of Ores
Liquid-Phase Metal Processing
Metal Enrichment Operations
Final Metal or Compound Recovery

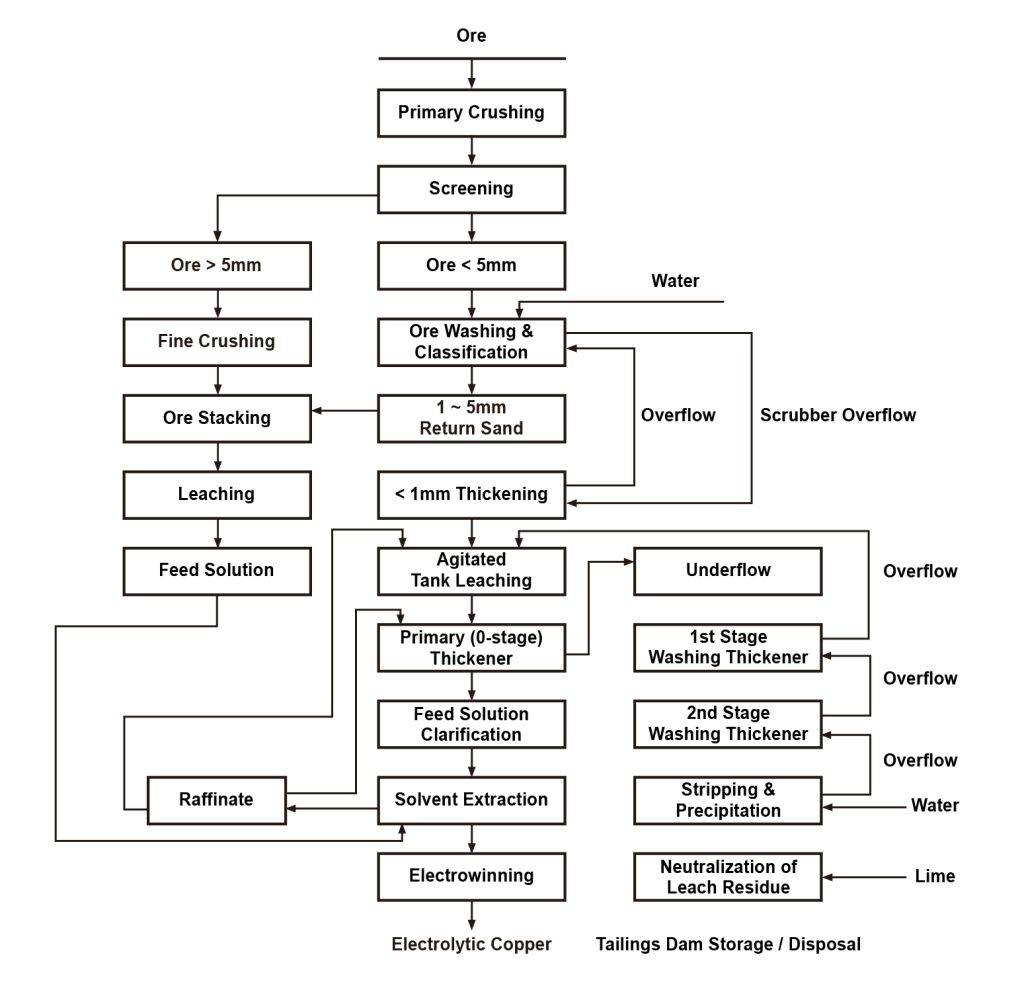
Hydrometallurgy is a process where ores undergo chemical reactions to transfer valuable metals from the raw materials into the liquid phase. Subsequently, the various valuable metals contained in the liquid phase are separated and enriched, and finally recovered in the form of metals or other compounds.
Solution
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is primarily used for solid-liquid separation in hydrometallurgy, including processes such as the separation of leachate and leaching residues, countercurrent washing of precious metal leaching residues, and purification of leachate.
| Product Name | Performance Features | Applicable Range |
| Anionic Polyacrylamide | Molecular weight: 8 to 20 million; hydrolysis degree: low, medium, or high | Generally suitable for neutral and alkaline slurry environments |
| Nonionic Polyacrylamide | Molecular weight: 6 to 12 million; extremely low hydrolysis degree | Acidic slurries, widely used in hydrometallurgical applications |



